Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Emotion dysregulation treatment includes evidence-based therapies like Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), along with practical skills training in mindfulness, distress tolerance, and emotional awareness. Treatment also involves lifestyle changes such as improved sleep, balanced nutrition, and regular exercise, combined with professional support systems including counseling, family therapy, and sometimes medication.
Quick Treatment Overview:
- Therapy-Based Approaches – DBT, CBT, ACT, Schema Therapy, and Mentalization-Based Treatment
- Skills Training – Mindfulness, breathing exercises, distress tolerance, cognitive reappraisal
- Lifestyle Support – Sleep hygiene, nutrition, physical activity
- Professional Help – Counseling, family therapy, support groups, medication when needed
- At-Home Strategies – Self-compassion practices, emotional awareness building, TIPP skills
You’re watching your child struggle with emotions that seem too big for their body. One moment they’re fine, and the next they’re melting down over something small. Or maybe they shut down completely when overwhelmed, going numb or pulling away. You’ve tried everything you can think of, but nothing seems to stick.
You’re not alone. I talk with parents every day who say, “I don’t even recognize my child in these moments.” Emotional dysregulation is when your child has difficulty managing their emotions and reactions in a way that fits the situation. It’s different from normal emotional responses because the feelings are more intense, last longer, and happen more often than you’d expect.
Here’s what emotional dysregulation can look like:
- Intense reactions that seem out of proportion to the trigger
- Rapid mood swings with no clear reason
- Acting impulsively without thinking about consequences
- Trouble calming down after getting upset
- Frequent irritability or anxiety
- Saying or doing things they later regret
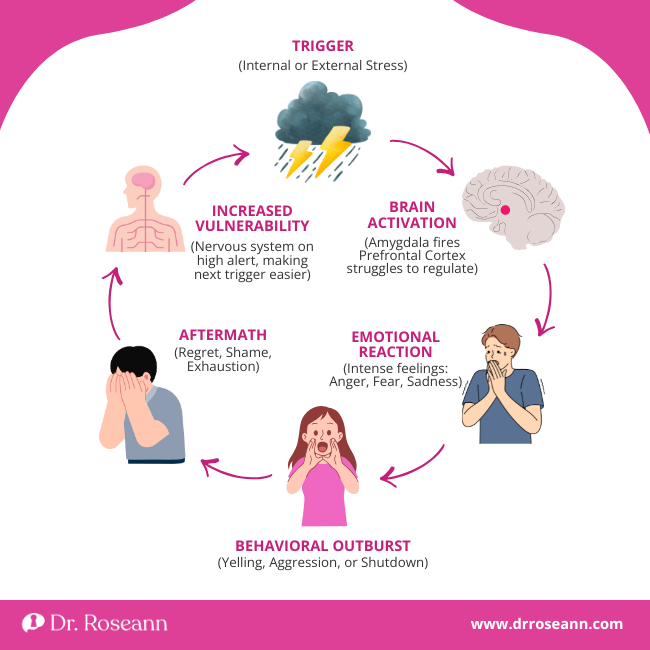
Behavior is communication. When your child has big emotional outbursts or shuts down, they’re not trying to make your life harder. Their nervous system is overwhelmed, and they don’t yet have the tools to regulate it.
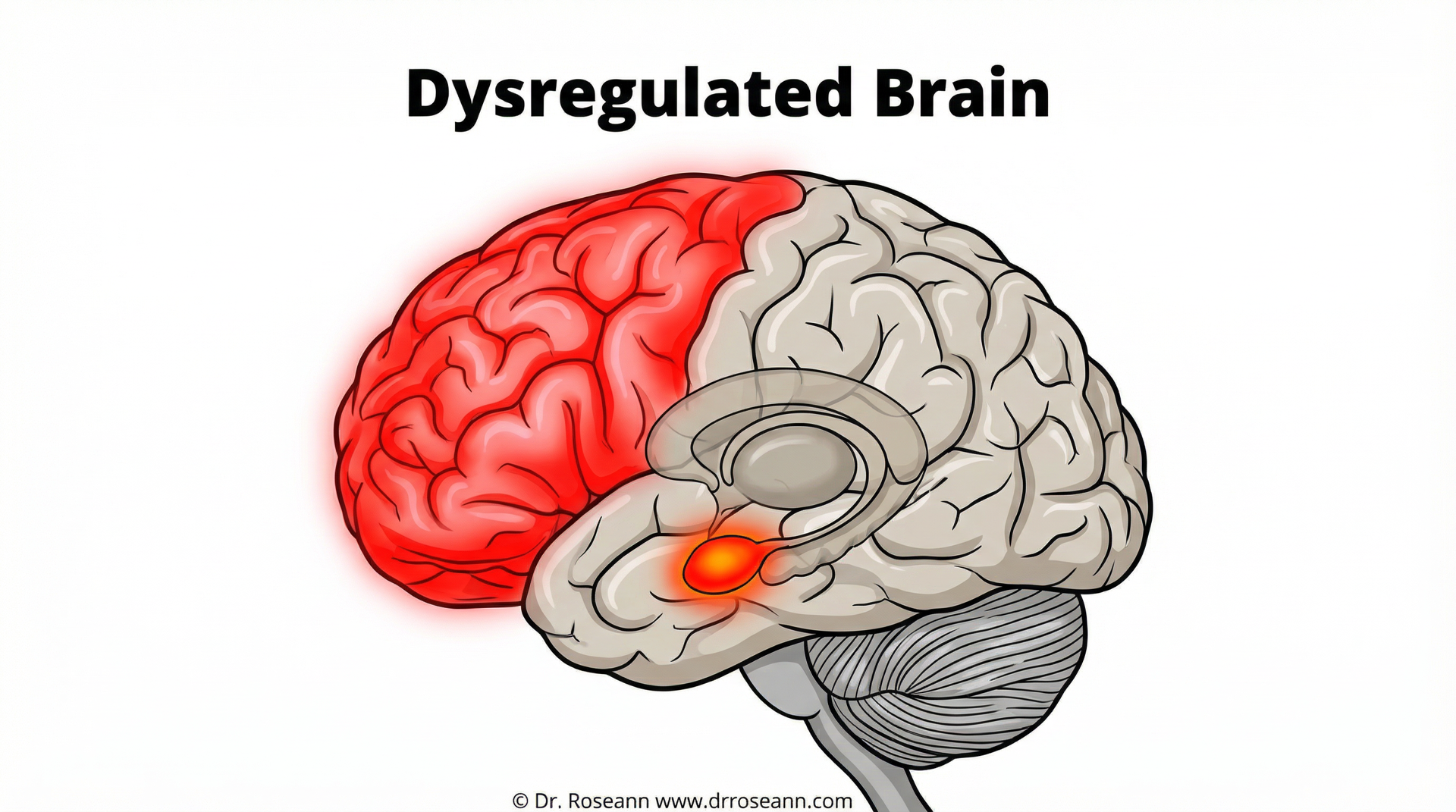
Research shows that emotional dysregulation isn’t just about missing early coping skills. It can develop from trauma, stress, genetic factors, or co-occur with conditions like ADHD, autism, anxiety, or mood disorders. The limbic regions of the brain (including the amygdala and insula) are linked to emotional reactivity, while the prefrontal regions help with emotional awareness and regulation. When these systems aren’t working together smoothly, dysregulation happens.
The good news? Emotion dysregulation treatment works. With the right combination of therapy, skills training, and support, your child can learn to manage their emotions more effectively. And you can learn strategies to help them in the moment and prevent future meltdowns.
I’m Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, and for over 30 years, I’ve specialized in helping children with emotional dysregulation, ADHD, anxiety, and other neurodevelopmental challenges using science-backed, natural solutions. My approach to emotion dysregulation treatment focuses on one key principle: Let’s calm the brain first so kids can build the skills they need to regulate their emotions and thrive. Together, we focus on practical, doable steps that support the whole child—and the whole family.
Emotion dysregulation treatment vocabulary:
- behavioral dysregulation definition
- dysregulated behavior examples
Your Complete Guide to Emotion Dysregulation Treatment
When we talk about emotion dysregulation treatment, we’re not just looking at surface-level behaviors. We’re diving deep into the root causes and building a comprehensive plan to help your child find emotional balance. It’s about creating lasting change, not just quick fixes.
As a parent, you want to know: Why is this happening, and what can I actually do that works? This guide walks you through the science in plain language and, more importantly, gives you clear action steps you can start using today.
The “Why” Behind the Outbursts: Causes and Co-occurring Conditions
Understanding why your child struggles with big emotions is the first step toward effective emotion dysregulation treatment. It’s rarely one single factor, but rather a complex interplay of biology, environment, and psychology.
Underlying Causes
- Biological Factors: Our brains are incredible, but sometimes certain areas don’t communicate as smoothly as they should. The limbic regions, including the amygdala and insula, are like the brain’s alarm system, responsible for sensing and reacting to emotions. The prefrontal regions, on the other hand, are the brain’s “wise leaders,” responsible for awareness, experience, and regulation. According to scientific research on the brain and emotion (Powers et al., 2017), a disruption in the prefrontal cortex can play a significant role in emotional dysregulation. We also know that genetics can play a part; the World Journal of Psychiatry notes that certain genetic variations (like alleles of the 5-HTTLPR gene polymorphism) have been associated with traits linked to emotion dysregulation.
- Environmental Factors: A child’s environment profoundly shapes their emotional development. Early childhood trauma, neglect, or even chronic stress can leave a lasting imprint on the nervous system, making it harder to manage emotions (Fan & Kang, 2025). When a child experiences repeated overwhelming situations without adequate support, their brain can become wired for hyper-reactivity.
- Psychological Factors: Existing mental health conditions often involve emotional dysregulation. These can include anxiety, depression, or other challenges that impact how a child perceives and responds to the world.
Co-occurring Conditions
Emotional dysregulation doesn’t usually exist in a vacuum. It’s often a prominent feature of various neurodevelopmental and mental health conditions. Effective emotion dysregulation treatment often means addressing these co-occurring conditions simultaneously.
- ADHD: While primarily known for challenges with attention and hyperactivity, emotional dysregulation is increasingly recognized as a significant component of ADHD. Scientific research on ADHD and emotional dysregulation points to emotional dysregulation as a fourth core symptom of ADHD (Soler-Gutiérrez et al., 2023). Children with ADHD may experience intense emotions that are difficult to manage, struggle to express them, and find it hard to shift focus away from strong feelings.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Children with ASD are often associated with amplified emotional responses and poor emotional control, as noted by the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. This can lead to difficulty using effective regulation strategies and impulsive reactions.
- Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD): Cureus highlights that emotional dysregulation and impulsivity are common features of BPD, and this can significantly impact relationships and self-image.
- Other Conditions: Emotional dysregulation is also frequently seen in conditions like Bipolar Disorder, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), Anxiety Disorders, Depression, Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder (DMDD), and even Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD). In all these cases, emotion dysregulation treatment needs to be custom to the individual’s unique presentation and underlying conditions.
Proven Therapies: The Core of Emotion Dysregulation Treatment
When it comes to effective emotion dysregulation treatment, evidence-based therapies are our superheroes. These approaches teach specific skills and strategies to help children and adolescents understand, manage, and respond to their emotions in healthier ways.
| Therapy | Key Focus for Kids | Main Skills Taught |
|---|---|---|
| Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) | DBT helps kids who feel emotions very intensely. It teaches them that it’s okay to have strong feelings (acceptance) but also gives them tools to change how they react to them (change). It’s about finding a balance. | Mindfulness: Staying in the present moment. Distress Tolerance: Getting through tough moments without making them worse. Emotion Regulation: Understanding and managing emotions. Interpersonal Effectiveness: Communicating needs and maintaining relationships. |
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | CBT focuses on the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. For kids, it’s about becoming a “thought detective” to catch unhelpful thoughts and challenge them, leading to calmer feelings and better choices. | Cognitive Restructuring: Identifying and changing negative thought patterns. Behavioral Activation: Engaging in positive activities to improve mood. Problem-Solving Skills: Learning to tackle problems step-by-step. |
| Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) | ACT helps kids stop struggling against their difficult thoughts and feelings. Instead of fighting them, they learn to notice and accept them, creating space to focus on what truly matters to them (their values). | Acceptance/Willingness: Making room for uncomfortable feelings without trying to change them. Cognitive Defusion: Seeing thoughts as just thoughts, not facts. Values-Based Action: Taking steps toward a meaningful life, even when it’s hard. |
- Schema Therapy: This therapy goes deeper to address long-standing negative patterns (or “schemas”) that often begin in childhood. It helps children understand where these patterns came from and develop healthier ways of thinking and behaving.
- Mentalization-Based Treatment (MBT): MBT helps children and teens understand their own mental states and the mental states of others. It improves their ability to “mentalize,” or see themselves from the outside and others from the inside, which is crucial for managing emotional reactions and improving relationships.
Dr. Roseann’s Therapist Quick Tip
In my 30+ years of clinical practice, I’ve learned that pervasive emotional dysregulation isn’t a behavior problem—it’s a nervous system stuck in survival mode.
Here’s what I tell parents:
Focus on calming the brain first, not correcting the behavior. When a child is chronically dysregulated, their brain can’t access logic, language, or coping skills—so discipline alone will always fall flat. Regulation has to come before expectations.
Try this today:
Create a daily predictable calming anchor—the same time, same activity, same order (for example: snack → movement → deep pressure → quiet time).
Why it works:
Predictability and sensory input signal safety to the nervous system, helping shift the brain out of fight-or-flight and into a regulated state where learning and emotional control are possible.
Remember:
Your child isn’t giving you a hard time—they’re having a hard time. When you lead with regulation, real healing can begin.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my child needs emotion dysregulation treatment and not just better discipline?
If your child’s reactions are frequent, intense, and long-lasting compared to other kids their age, and typical discipline strategies don’t help (or make things worse), it’s a sign this is about regulation, not “bad behavior.” Remember, behavior is communication. When we see it through that lens, we shift from punishment to support—and that’s where real change happens.
Where should I start if my child is completely overwhelmed and melting down daily?
Let’s calm the brain first. That means focusing on nervous system regulation before expecting your child to use higher-level coping skills. Start with predictable routines, sleep support, movement, hydration, and simple calming tools like breathing or sensory breaks. As the brain gets calmer, therapy and skills training become much more effective.
Can emotion dysregulation treatment help if my child has ADHD, ASD, or anxiety too?
Yes. Emotional dysregulation is often a core part of ADHD, ASD, anxiety, OCD, mood disorders, and PANS/PANDAS. The most effective treatment plans address both the underlying condition and the regulation challenges at the same time. With the right strategies, kids can learn to manage big feelings, improve behavior, and function better at home and school.
How long does it take to see progress with emotion dysregulation treatment?
That depends on the child, the severity of symptoms, and how consistently supports are used at home and school. Many families notice small but meaningful changes within a few weeks of calming-the-brain strategies and targeted therapy, with bigger shifts happening over months. Progress is rarely a straight line, but with the right plan, kids do get better.
What can I do at home to support my child’s treatment?
You are a powerful part of your child’s healing. At home, focus on staying calm yourself, using co-regulation (your calm helps calm their brain), creating predictable routines, and responding to behavior with curiosity instead of judgment. Ask, “What is this behavior communicating?” Partner with your providers, practice the skills your child is learning in therapy, and remember—you’re not alone in this.
Citations
Fan, L. and Kang, T. (2025). Early childhood trauma and its long-term impact on cognitive and emotional development: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Med, 57(1):2536199. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2025.2536199.
Powers, A., Stevens, JS., van Rooij, SJH., Ely, TD., Fani, N., Jovanovic, T., Ressler, KJ., and Bradley, B. (2017) Neural correlates and structural markers of emotion dysregulation in traumatized civilians. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 12(5):823-831. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsx005.
Soler-Gutiérrez, AM., Pérez-González, JC., and Mayas, J. (2023) Evidence of emotion dysregulation as a core symptom of adult ADHD: A systematic review. PLoS One, 18(1):e0280131. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0280131.
Always remember… “Calm Brain, Happy Family™”
Disclaimer: This article is not intended to give health advice and it is recommended to consult with a physician before beginning any new wellness regime. *The effectiveness of diagnosis and treatment vary by patient and condition. Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC does not guarantee certain results.
Are you looking for SOLUTIONS for your struggling child or teen?
Dr. Roseann and her team are all about science-backed solutions, so you are in the right place!